Answer Key
Module 4: Quiz
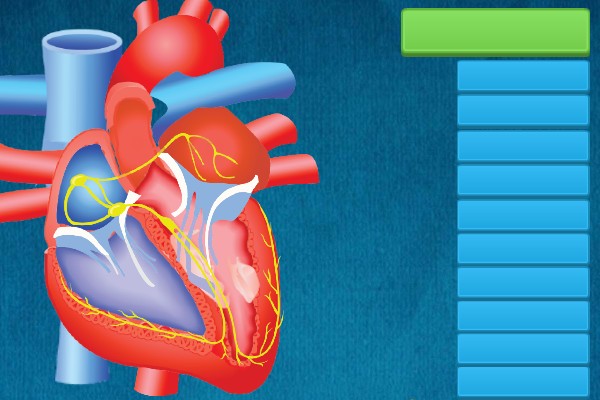
1.
-
Pulmonary Artery -

Aorta -
Descending Aorta -
Coronary Artery -
Middle Cerebral Artery
2.
-
2 - 1 Atrium, 1 Ventricle -
3 - 1 Atrium, 2 Ventricles -
3 - 2 Atria, 1 Ventricle -

4 - 2 Atria, 2 Ventricles
3.
-

True -
False
4.
-
True -

False
5.
-

Between the right atrium and the right ventricle -
Between the left atrium and left ventricle -
Between the right ventricle and the pulmonary artery -
Between the left ventricle and the aorta
6.
-

Pulmonary arteries -
Pulmonary veins
7.
-
Pulmonary arteries -

Pulmonary veins
8.
-
Tricuspid valve -

Pancreas -
Vena cava
U.S. Standards
- NGSS-Science: MS.LS1.3
- CCSS-Math: MP.1
- CCSS-ELA: SL.6.1, SL.7.1, SL.8.1
- CSTA: 2-AP-13, 2-AP-16, 2-AP-17
- CS CA: 6-8.AP.13, 6-8.AP.16, 6-8.AP.17
- ISTE: 1.c, 1.d, 4.d, 5.c, 5.d, 6.b
U.K. Standards
Key stage 3
Pupils should be taught to:- design, use and evaluate computational abstractions that model the state and behaviour of real-world problems and physical systems
- create, reuse, revise and repurpose digital artefacts for a given audience, with attention to trustworthiness, design and usability
- understand a range of ways to use technology safely, respectfully, responsibly and securely, including protecting their online identity and privacy; recognise inappropriate content, contact and conduct, and know how to report concerns
Description
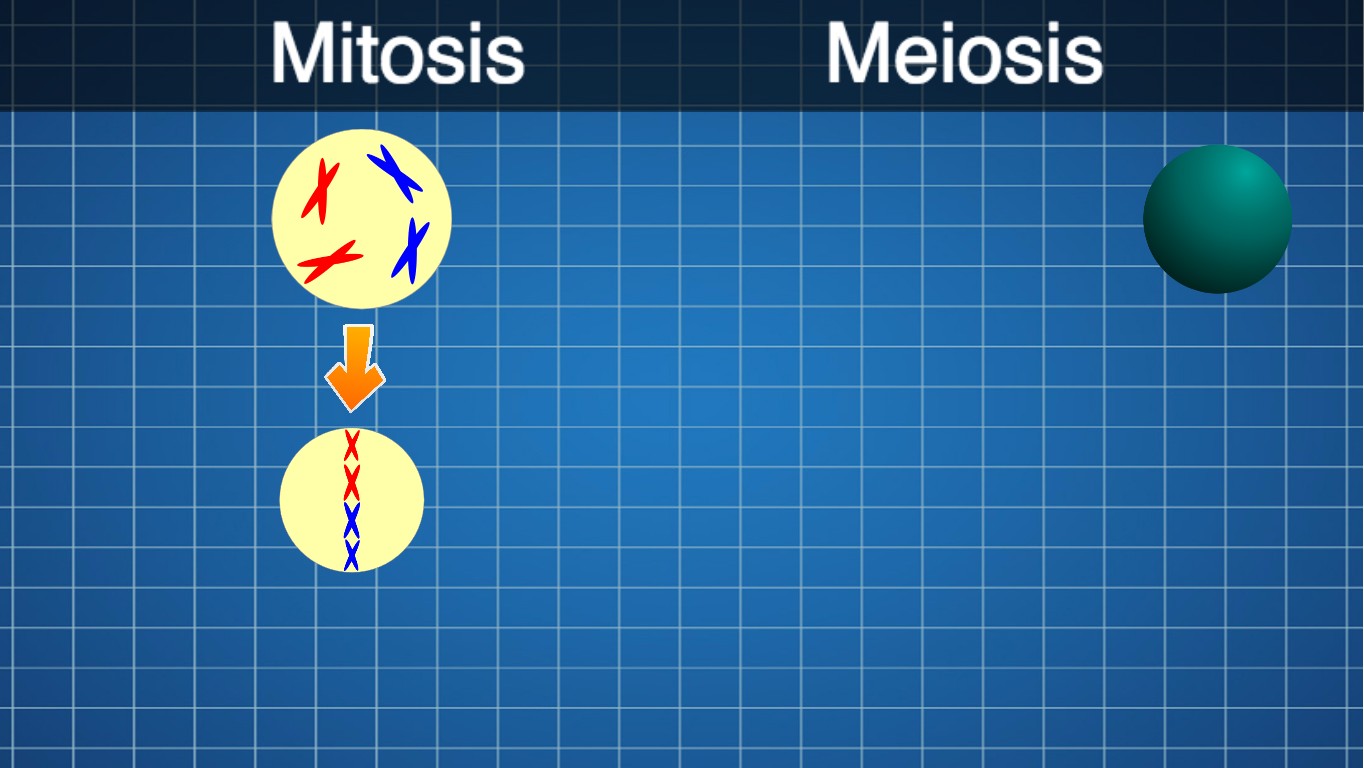
Once your students have completed at least five lessons of Programming 101 or equivalent coding experience, you can assign these NGSS-aligned projects to complement your teaching on topics in biology, anatomy, and genetics. For example, if you’re teaching a lesson on cell division, you can assign the mitosis and meiosis. Your students will draw their own animations and use coding and outside research to demonstrate mitosis and meiosis, while comparing and contrasting the two processes.
With this collection of life science projects, you can easily integrate coding and project-based learning into your curriculum. Each STEM lesson walks students through how to make a project about something they’re learning in school with step-by-step instructions. At each step, it encourages them to make their project unique and interesting, emphasizing that coding is a creative medium much like writing or drawing.
We’re constantly updating our STEM courses with new projects, so if there’s something you’d like us to add, send us a message at support@tynker.com.
What Students Learn
- Use programming for science projects
- Build a slide show on a topic
- Build a quiz game
- Make an interactive charts and models
- Use animation to illustrate
- Narrate using your own voice
- Use the physics engine to model
- Troubleshoot and debug programs
Technical Requirements
* Online courses require a modern desktop computer, laptop computer, Chromebook, or Netbook with Internet access and a Chrome (29+), Firefox (30+), Safari (7+), or Edge (20+) browser. No downloads required.
* Tablet courses require an iPad (iOS 10+) with Tynker or Tynker Junior app installed and Internet access