Answer Key
U.S. Standards
- CCSS-ELA: SL.8.1, RI.9-10.3, RI.9-10.6, RI.11-12.3, RI.11-12.6, L.9-10.3, L.9-10.6, L.11-12.3, L.11-12.6
- CCSS-Math: HSN.Q.A.2, HSN.Q.A.3, MP.1, MP.2
- CSTA: 2-AP-13, 2-AP-16, 2-AP-17, 2-AP-19, 3A-AP-17, 3B-AP-11
- CS CA: 6-8.AP.13, 6-8.AP.16, 6-8.AP.17, 6-8.AP.19, 9-12.AP.12, 9-12.AP.16
- ISTE: 1.c, 1.d, 4.d, 5.c, 5.d, 6.b
U.K. Standards
Key stage 3
Pupils should be taught to:- design, use and evaluate computational abstractions that model the state and behaviour of real-world problems and physical systems
- understand several key algorithms that reflect computational thinking [for example, ones for sorting and searching]; use logical reasoning to compare the utility of alternative algorithms for the same problem
- undertake creative projects that involve selecting, using, and combining multiple applications, preferably across a range of devices, to achieve challenging goals, including collecting and analysing data and meeting the needs of known users
- create, reuse, revise and repurpose digital artefacts for a given audience, with attention to trustworthiness, design and usability
- understand a range of ways to use technology safely, respectfully, responsibly and securely, including protecting their online identity and privacy; recognise inappropriate content, contact and conduct, and know how to report concerns
Key stage 4
All pupils must have the opportunity to study aspects of information technology and computer science at sufficient depth to allow them to progress to higher levels of study or to a professional career. Pupils should be taught to:- develop their capability, creativity and knowledge in computer science, digital media and information technology
- develop and apply their analytic, problem-solving, design, and computational thinking skills
- understand how changes in technology affect safety, including new ways to protect their online privacy and identity, and how to report a range of concerns
Description
Learn Python like the pros! Students master Python programming including I/O, data types, math operators, loops, strings, lists, functions, dictionaries, classes, objects, and recursion.
Topics Covered: Python syntax, variables, data types, math operators, boolean logic, Turtle graphics, branching, while loops, strings, lists, for loops, functions, dictionaries, classes and objects, and recursion.
What Students Learn
- Learn Python syntax
- Use conditional logic, loops, and conditional loops to solve problems
- Create and use variables
- Write and interpret Python expressions
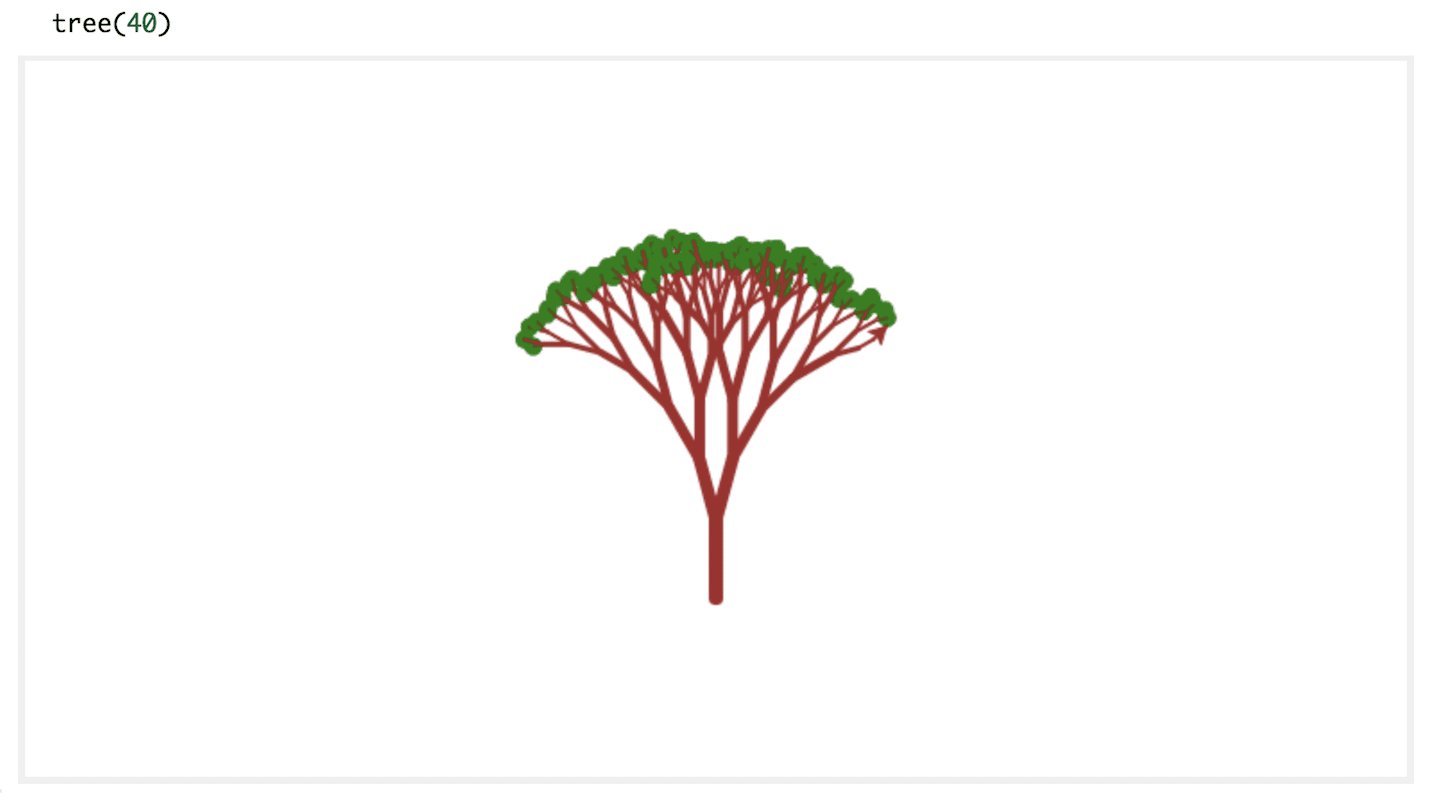
- Use pen drawing and Turtle graphics to draw shapes and display images
- Use arrays, dictionaries, and objects to store structured data
Technical Requirements
* Online courses require a modern desktop computer, laptop computer, Chromebook, or Netbook with Internet access and a Chrome (29+), Firefox (30+), Safari (7+), or Edge (20+) browser. No downloads required.